Microsoft uses virtualization in Windows 11 for scenarios including Hypervisor-protected code integrity (HVCI), also called memory integrity, and the Virtual Machine Platform (VMP).
VMP provides core virtual machine services for Windows. Memory integrity helps prevent attackers from injecting their own malicious code and helps ensure that all drivers loaded onto the OS are signed and trustworthy. It will be enabled by default on all new Windows 11 devices. Enabling security features on by default is based on the evolving threat landscape and the responsibility Microsoft has to protect over a billion Windows users.
As part of continued testing and feedback from users, Microsoft has seen that in some scenarios and some configurations of gaming devices there may be a performance impact with memory integrity and VMP on.
Windows provides choice and control for users to configure their PCs to meet their specific needs, including the ability to turn Windows features like memory integrity and VMP on and off. Gamers who want to prioritize performance have the option to turn off these features while gaming and turn them back on when finished playing. However, if turned off, the device may be vulnerable to threats.
Below are instructions to turn off these features.
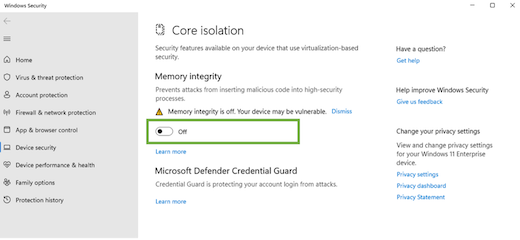
Turning off memory integrity
-
Select Start , enter ‘Core Isolation’ in the taskbar, and select Core Isolation from the list of results to open the Windows security app.
-
On the Core isolation page, turn off the toggle for Memory integrity. You might need to restart your device.
Turning off Virtual Machine Platform (VMP)
-
Select Start , enter ‘Windows features’ in the search box, and select Turn Windows features on or off from the list of results.
-
In the Windows Features window that just opened, find and unselect Virtual Machine Platform.

-
Select OK. You might need to restart your device.










