You can bring data from one Access database into another in many ways. Copying and pasting is the simplest method, but importing and linking offer you better control and flexibility over the data that you bring, and over how you bring that data into the destination database.
This article explains how to import or link to data in another Access database.
What do you want to do?
Understand importing and linking to data from another Access database
When you import from another database, Access creates a copy of the data in the destination database without altering the source. During the import operation, you can choose the objects you want to copy, control how tables and queries are imported, specify whether relationships between tables should be imported, and so on.
You might want to import data for example to create some tables that are similar to tables that exist in another database. You might want to copy the entire table or just the table definitions to avoid manually designing each of these tables. When you choose to import only the table definition, you get an empty table. In other words, the fields and field properties are copied to the destination database, but not the data in the table. Another advantage of importing (compared to a copy-paste operation) is that you can choose to import the relationships between the tables along with the tables themselves.
If your goal is to add records from one database to an existing table in another database, you should consider importing the records to a new table and then creating an append query. You cannot append records to an existing table during an import operation. For more information about append queries, see the article Add records to a table by using an append query.
You might want to link to data in another Access database if your organization uses several Access databases, but data in some tables, such as Employees, need to be shared between various databases. Instead of duplicating the table in each such database, you can keep the table in a single database and link to it from other databases. Another workgroup or department needs to be able to add to and use the data in your database, but you want to continue to own the structure of the tables.
Import data from another Access database
The process of importing data follows these general steps:
-
Prepare for the import operation
-
Run the Import Wizard
-
Optionally save the import settings as an import specification for later reuse
The following sets of steps explain how to perform each action.
Prepare for the import operation
-
Locate the source database and identify the objects that you want to import.
If the source database is an .mdb or .accdb file, you can import tables, queries, forms, reports, macros, and modules. If the source file is an .mde or .accde file, you can import only tables.
-
If this is the first time you are importing data from an Access database, refer to the following table for some useful tips.
Element
Description
Multiple objects
You can import multiple objects in a single import operation.
New object
Each import operation creates a new object in the destination database. You cannot overwrite an existing object or append records to an existing table by using an import operation.
Importing a linked table
If the source table (for example, Employees1 in the Sales database) is actually a linked table (a table that links to the Employees table in the Payroll database), the current import operation is replaced by a linking operation. At the end of the operation, you will see a linked table (named, for example, Employees1) that links to the original source table (Employees in the Payroll database).
Skipping fields and records
You cannot skip specific fields or records when importing data from a table or query. However, if you do not want to import any of the records in a table, you can choose to import only the table definition.
Relationships
You can choose to import the relationships between source tables.
Table definition
You can choose to import an entire table or just the table definition. When you import just the definition, Access creates a table that has the same fields as the source table, but no data.
Lookup fields
If a field in the source table looks up values in another table or query, you must import the related table or query if you want the destination field to display lookup values. If you do not import the related table or query, the destination field will only display the lookup IDs.
Queries
You can import a query either as a query or as a table. If you import a query as a query, then you must import the underlying tables.
-
Close the source database. Ensure that no user has it open in exclusive mode.
-
Open the destination database. Ensure that the database is not read-only and that you have the necessary permissions to add objects and data to the database.
If the source database is password protected, you are prompted to enter the password each time you use it as a source for an import operation.
Note: If you want to import the data into a new database, you must create a blank database that does not contain any tables, forms, or reports before starting the import operation.
The import operation does not overwrite or modify any of the existing tables or objects. If an object with the same name as the source object already exists in the destination database, Access appends a number (1, 2, 3, and so on) to the name of the import object. For example, if you import the Issues table to a database that already has a table named Issues, the imported table will be named Issues1. If the name Issues1 is already in use, the new table will be named Issues2, and so on.
It is important to note that if you want to append the records in the source table to a table in the destination database, you must use an append query instead of running an import operation. For more information about append queries, see the article Add records to a table by using an append query.
Import the data
-
The location of the import wizard differs slightly depending upon your version of Access. Choose the steps that match your Access version:
-
If you're using Microsoft 365, Access 2021, or Access 2019 on the External Data tab, in the Import & Link group, click New Data Source > From Database > Access.
-
If you're using Access 2016, on the External Data tab, in the Import & Link group, click Access.
-
-
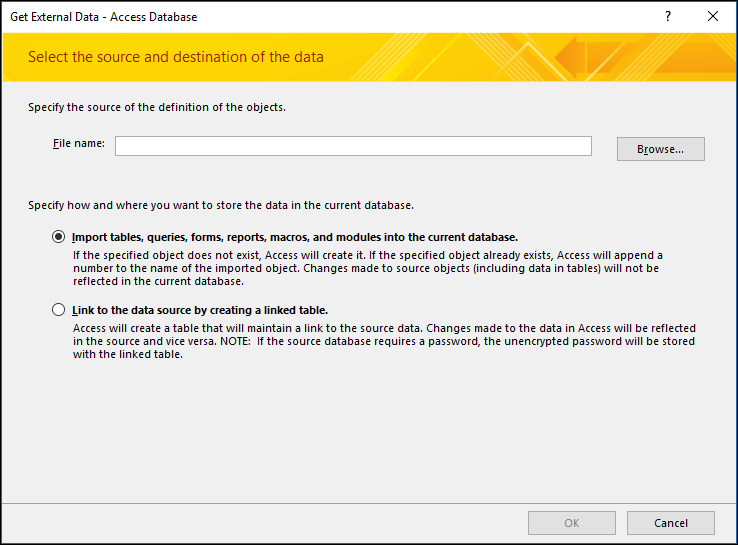
The Get External Data - Access Database import and link wizard opens.
-
In the File name text box, type the name of the source database or click Browse to display the File Open dialog box.
-
Select Import tables, queries, forms, reports, macros, and modules into the current database and click OK.
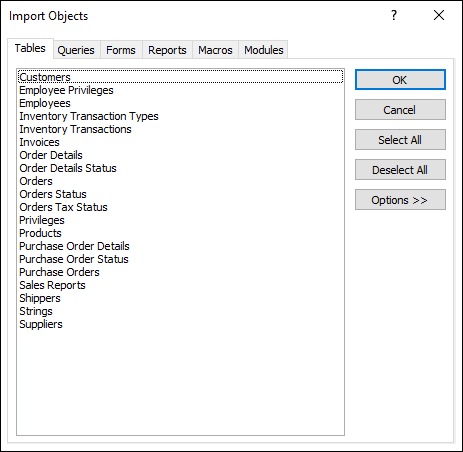
The Import Objects dialog box opens.
-
In the Import Objects dialog box, on the Tables tab, select the tables you want to import. If you want to import queries, click the Queries tab and select the queries you want to import.
To cancel a selected object, click the object again.
-
Click Options to specify additional settings.
The following table describes how each option impacts the results of the operation.
Element
Description
Relationships check box
Select to import the relationships between the selected tables.
Menus and Toolbars check box
Select to import any custom menus and toolbars that exist in the source database. The menus and toolbars are displayed on a tab named Add-Ins.
Import/Export Specs check box
Select to import any saved import or export specifications that exist in the source database.
Nav Pane Groups check box
Select to import any custom Navigation pane groups that exist in the source database.
Definition and Data option button
Select to import the structure and data of all selected tables.
Definition Only option button
Select to import only the fields in the selected tables. The source records are not imported.
As Queries option button
Select to import the selected queries as queries. In this case, remember to import all the underlying tables along with the queries.
As Tables option button
Select to import queries as tables. In this case, you need not import the underlying tables.
-
Click OK to finish the operation.
Access copies the data and displays error messages if it encounters any problems. If the operation succeeds in importing the data, the final page of the wizard allows you to save the details of the operation as an import specification for future use.
Link to data in another Access database
Linking lets you connect to data in another database without importing it, so that you can view and modify the latest data in both the source and destination databases without creating and maintaining two copies of the same data. You can link only to tables in another Access database. You cannot link to queries, forms, reports, macros, or modules.
When you link to a table in an Access database, Access creates a new table, called a linked table, which maintains a link to the source records and fields. Any changes you make to the data in the source database are reflected in the linked table in the destination database, and vice versa. However, you cannot change the structure of a linked table in the destination database. In other words, you cannot make changes to a linked table such as adding or deleting a field, or modifying the data type of a field.
The process of linking to data in another Access database follows these general steps:
-
Prepare for the link operation
-
Run the Link Wizard
The following sets of steps explain how to perform each action.
Prepare to link tables in an Access database
-
Locate the source database.
The file format can be MDB, MDE, ACCDB, or ACCDE. If the source database is password protected, you will be prompted to enter the password during the linking operation.
-
Identify the tables to which you want to link. You can link to tables, but you cannot link to queries, forms, reports, macros, or modules. If this is the first time you are linking to tables in another Access database, refer to the following table for some useful tips.
Element
Description
Multiple objects
You can create links to multiple tables in a single linking operation. A linked table is created for each source table.
Linked tables as source
You cannot link to a table that is already a linked table in the source database.
For example, if the Employees1 table that you want to link to in the Sales database is actually a linked table that links to the Employees table in the Payroll database, you cannot use the Employees1 table in the Sales database as the source table. You should instead link directly to the Employees table in the Payroll database.
New or existing table
Each linking operation creates a new linked table for each source table. You cannot overwrite or append to an existing table by using a linking operation.
Relationships
If you select multiple source tables, the relationships between the tables are automatically carried forward to the destination database. However, you cannot change or delete the relationship in the destination database.
Lookup fields
If a field in the source table looks up values in another table, you must remember to link to the related table if you want the destination field to display lookup values. If you do not link to the related table or query, the destination field only displays the lookup IDs.
-
Close the source database. Ensure that no other user has the database open in exclusive mode.
-
Open the destination database. Ensure that the destination database is not read-only and that you have the necessary permissions to add objects and data to the database.
Note: If you want to create the links in a new database, you must create a blank database (one that does not contain any tables, forms, or reports) before starting the link operation.
The operation does not overwrite or modify any of the existing tables or objects. If an object with the same name as the source object already exists in the destination database, Access appends a number (1, 2, 3, and so on) to the name of the linked table. For example, if you link to the Issues table from a database that already has a table named Issues, the linked table will be named Issues1. If the name Issues1 is already in use, the new table will be named Issues2, and so on.
Remember that if you want to append the records in the source table to a table in the destination database, you must use an append query instead of running a linking operation.
For more information about append queries, see the article Add records to a table by using an append query.
Link to the data
-
The location of the link wizard differs slightly depending upon your version of Access. Choose the steps that match your Access version:
-
If you're using Microsoft 365, Access 2021, or Access 2019 on the External Data tab, in the Import & Link group, click New Data Source > From Database > Access.
-
If you're using Access 2016, on the External Data tab, in the Import & Link group, click Access.
-
-
The Get External Data - Access Database import and link wizard opens.

-
In the File name text box, type the name of the source database or click Browse to display the File Open dialog box.
-
Click Link to the data source by creating a linked table, and then click OK.
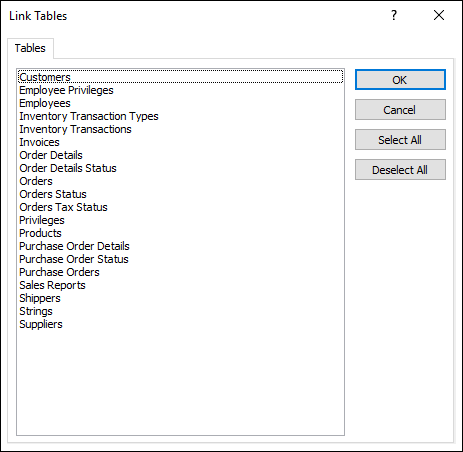
The Link Tables dialog box opens.
-
In the Link Tables dialog box, select the tables you want to link to.
To cancel a selection, click the table again.
-
Click OK to finish the operation.
Access creates the linked tables.
-
Open the linked tables in Datasheet view to ensure that the data looks correct.
What else should I know?
-
For information on how to save the details of your import into a specification that you can reuse later, see the article Save the details of an import or export operation as a specification.
-
For information on how to run saved import specifications, see the article Run a saved import or export operation.
-
For information on how to schedule specifications to run at specific times, see the article Schedule an import or export operation.
-
For information on how to change a specification name, delete specifications, or update the names of source files in specifications, see the article Manage Data Tasks.










